Gestational hypertension
During pregnancy the systemic vascular resistance falls, resulting in a lower blood pressure. Elevated blood pressure in a pregnant women is always pathological and can have consequences for the baby and the mother alike.
Etiologies
- Transient hypertension
- Can be seen in pregnant and non-pregnant patients
- One measurement of BP >140/80
- It is not sustained over long periods of time
- Labs
- No changes
- Complications
- None
- Management
- Ambulatory blood pressure log
- No medical treatment because not sustained
- Chronic hypertension
- Measurement of BP >140/80
- Sustained
- Shows up before 20 weeks gestation
- Labs
- No changes
- Complications
- None (acute)
- Management
- Need to treat medically
- Many antihypertensives are teratogens
- Methyldopa, labetalol (short-acting), hydralazine
- Can lead to pre-eclampsia
- Frequent creatinine, liver enzymes, U/A, fetal ultrasounds, follow-ups
- Gestational hypertension
- Measurement of BP >140/80
- Sustained
- Shows up after 20 weeks gestation
- Labs
- No changes
- Complications
- None (acute)
- Management
- Can lead to pre-eclampsia
- Frequent creatinine, liver enzymes, U/A, fetal ultrasounds, follow-ups
- Can lead to pre-eclampsia
- Pre-eclampsia
- Without severe features
- BP over 140/80
- Sustained after 20 weeks
- End organ damage present
- Proteinuria on urinalysis
- >300 mg/dL
- Proteinuria on urinalysis
- Complications
- Not severe (proteinuria is the main one)
- Management
- If term, go through with delivery = cures the Htn
- If preterm
- Don't deliver yet
- Frequent follow-ups
- Trend proteinuria and complications
- If worsening symptoms or proteinuria may have to treat medically
- With severe features
- BP over 160/110
- Sustained after 20 weeks
- End organ damage present
- Proteinuria on urinalysis
- >5g/dL
- Proteinuria on urinalysis
- Severe features
- Decreased platelets
- Transaminitis
- RUQ abdominal pain due to decreased blood flow
- Creatinine can be elevated
- Normal Cr in pregnancy is decreased (35-70 umol/L)
- Cr >97 or doubling of Cr in the absence of renal disease = abnormal
- Consider pre-eclampsia
- Vasoconstriction
- Pulmonary edema
- Chest pain
- Headaches
- Vision changes
- Management
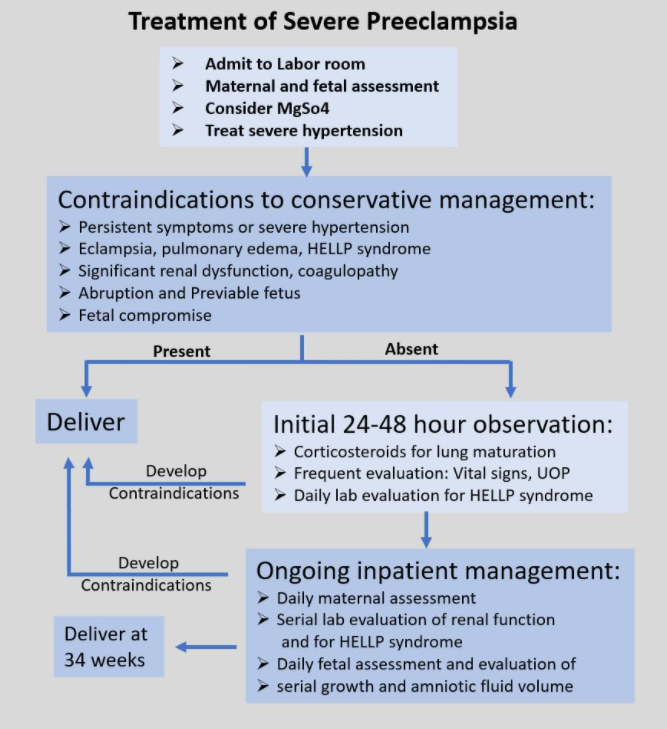
- Administer magnesium sulphate
- Go through with delivery
- Induced vaginal delivery
- Without severe features
- Eclampsia
- The patient will have seizures regardless of the BP
- No history of epilepsy
- Management
- Magnesium sulphate administration to stop the seizure
- Have to check for toxicity
- Decreased deep tendon reflexes is a sign
- Can lead to decreased respiratory drive
- Administer calcium gluconate to reverse toxicity
- Go through with delivery
- C-section - not much time available
- Magnesium sulphate administration to stop the seizure
- HELLP syndrome - a type of preeclampsia with severe features
- Hemolysis, Elevated Liver enzymes and Low Platelets
- Patients can have severe features
- Decreased platelets
- Transaminitis
- RUQ abdominal pain due to decreased blood flow
- Creatinine can be elevated
- Normal Cr in pregnancy is decreased (35-70 umol/L)
- Cr >97 or doubling of Cr in the absence of renal disease = abnormal
- Consider pre-eclampsia
- Vasoconstriction
- Pulmonary edema
- Chest pain
- Headaches
- Vision changes
- Management - same way as eclampsia
- Magnesium sulphate administration to stop the seizure

- Have to check for toxicity
- Decreased deep tendon reflexes is a sign
- Can lead to decreased respiratory drive
- Administer calcium gluconate to reverse toxicity
- Go through with delivery
- C-section - not much time available
- Magnesium sulphate administration to stop the seizure
All information provided on this website is for educational purposes and does not constitute any medical advice. Please speak to you doctor before changing your diet, activity or medications.
