Menopause
Menopause is defined as the permanent cessation of the monthly periods for at least 12 consecutive months. At this time the pituitary gonadotropins (FSH and LH) are elevated and ovarian follicular recruitment has stopped. Although smoking and hysterectomy are some factors for early menopause, most women go into menopause in their early 50s.
Perimenopause
The transition from normal menses to menopause. The average age for going into perimenopause is the mid-40s. 10% of women have abrupt perimenopause while the majority take 4-5 years to reach full menopause.
Symptoms
- Fat collection in the lower abdomen is common.
- Postmenopause the ovaries produce no estrogen and peripheral fat tissue takes over that function.
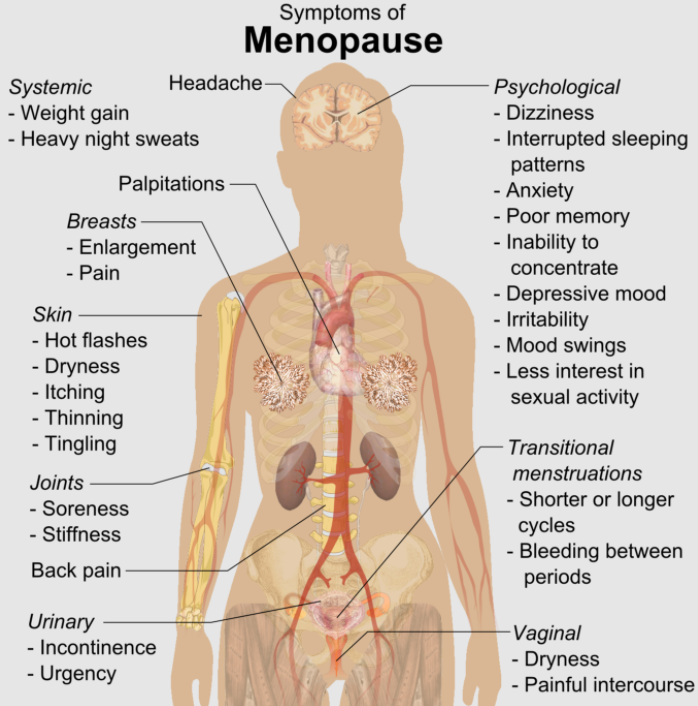
- Vasomotor instability
- Hot flashes affect majority of perimenopausal women
- Caused by falling estrogen levels
- Sudden increase in body temperature and rapid decline to normal
- Obese women may not experience severe hot flashes (due to peripheral adipose estrogen conversion)
- Advancing age also reduces the severity of these
- Osteoporosis
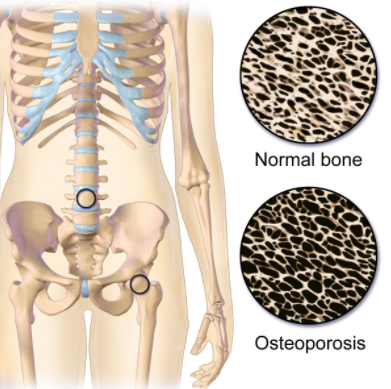
- Normally estrogen inhibits bone resorption
- Falling levels of estrogen put women at risk for osteoporosis
- On the bone density scan, many women fall within the osteopenic (-1 to -2.5) or osteoporotic region (<-2.5)
- 50% of women aged 70 or higher have vertebral fractures
- Bisphosphonates are something to consider in postmenopausal women
- Genital atrophy
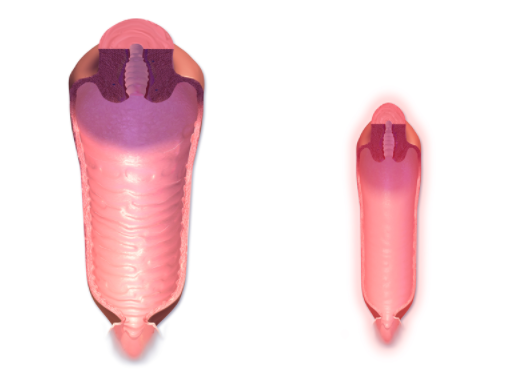
- Especially the lower genital organs will be affected
- Dyspareunia, urinary incontinence is common
- Mood issues
- No measurable effect
- Some women experience fatigue, anxiety and headaches during perimenopause but with no clear link to estrogen
Hormones
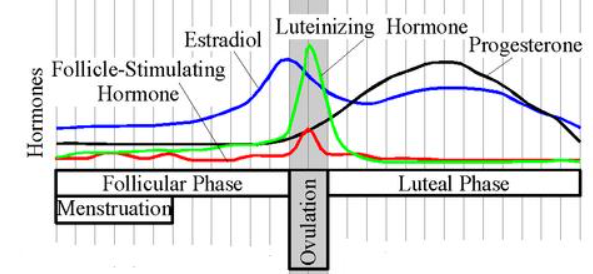
- FSH and LH
- FSH increases by 10-20 times
- LH increases 3 times
- Estrogen
- Sharp decrease due to ovarian dysfunction
- Peripheral adipose tissue produces almost all of estrogen postmenopause
- Androgens
- Elevated gonadotropins make the ovaries continue to make androgens
Hormone replacement
Some women opt for estrogen replacement therapy post-menopause to treat the symptoms of a hypoestrogenic state. This therapy has many benefits but also some risks.
- Benefits
- No hot flashes, osteoporosis, genital atrophy
- Risks
- Risk of endometrial hyperplasia (similar to tamoxifen therapy)
- The risk of breast cancer may be increased
- Progestin therapy can reduce the risk of endometrial hyperplasia
- Adverse effects
- Nausea, vaginal bleeding, breast tenderness
- Compliance
- Most of the benefits are achieved over the long term and as such compliance can be an issue
- Recently HRT has been discontinued due to the risks of endometrial hyperplasia, thromboembolism, stroke and breast cancer

All information provided on this website is for educational purposes and does not constitute any medical advice. Please speak to you doctor before changing your diet, activity or medications.
