Congestive heart failure exacerbation
We have to consider a few concepts to understand exacerbation in heart failure:
- Preload
- Amount of blood that comes into the heart
- Also known as the total volume flowing into the heart
- Afterload
- Resistance the heart has to work against to pump blood
- Also known as systemic vascular resistance
- Increased afterload will increase the preload through the renin-angiotensin system
- Salt and water absorption = increased preload
- Increased afterload will also further increase the afterload (positive feedback loop)
- Vasoconstriction
Presentation
The presentation of CHF exacerbation is heavily tied to the concepts outlined above. The patient's temperature is an indicator of afterload while their fluid status is an indicator of their preload.
| Warm | Cold | |
| Dry | Normal state |
Low flow state Uncommon Systemic vascular resistance/Afterload is increased |
| Treat with: Vasodilators | ||
| Wet |
Volume overload state Very common in decompensated CHF Etiology = diet, medication compliance
|
Cardiogenic shock Most dangerous state
|
|
Treat with: Use diuretics to reduce preload |
Treat with: Inotropes and vasodilators |
- Dry/Wet
- Classical sign - diagnostic with all 3 present
- Dyspnea on exertion
- Orthopnea
- PnD
- Increased weight
- Abdominal pain
- Physical exam
- Increased preload
- Elevated JVP
- Distended internal jugular vein
- Assess at 0, 30, 60, 90 degrees
- Hepatojugular reflux
- Peripheral edema
- Pulmonary crackles
- Investigations
- U/S
- Kerley B lines
- Chest x-ray
- BNP levels
- U/S
- Classical sign - diagnostic with all 3 present
- Warm/Cold
- Reduced systemic vascular resistance = Reduced organ perfusion
- Brain
- Fatigue
- Somnolence
- Kidney
- Brain
- Physical exam
- Palpation with the back of hand for temperature (on wrist and ankles)
- Investigations
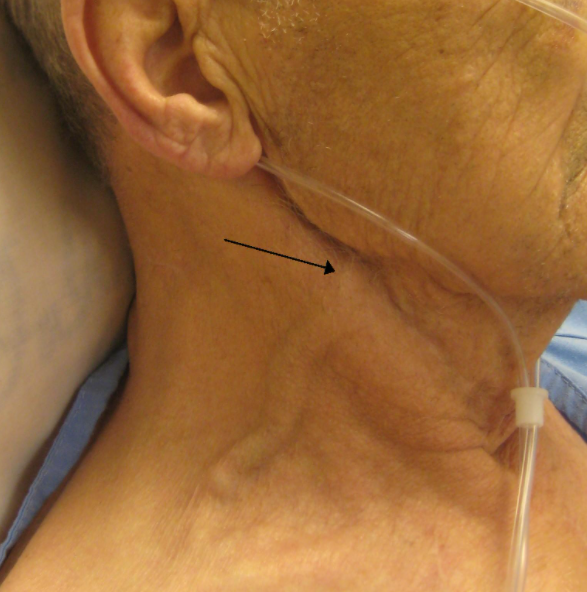
- Pulsus alternans on ECG
- Reduced systemic vascular resistance = Reduced organ perfusion
Treatment
- Wet and warm
- Diuresis
- 2.5 times the oral home dose as IV
- The goal is to lose 3L on day one, and 1L daily thereafter
- Boluses are just as effective as constant infusions
- Assess for urinary output
- Diuresis
- Dry and cold
- Vasodilation
- IV rapid onset ACEi
- IV hydralazine
- Vasodilation
- Wet and cold
- Vasodilation
- IV rapid onset ACEi
- IV hydralazine
- Inotropes > increased contractility and vasodilation
- Dobutamine
- Milrinone
- Diuretics
- Only after the kidneys are perfused = warm skin
- Vasodilation
Beta-blockers should not be initiated during an exacerbation as they will reduce contractility and increase mortality. They are however used in the chronic management of heart failure as shown in the previous post.
All information provided on this website is for educational purposes and does not constitute any medical advice. Please speak to you doctor before changing your diet, activity or medications.
All information provided on this website is for educational purposes and does not constitute any medical advice. Please speak to you doctor before changing your diet, activity or medications.
